However, dealing with enormous amounts of data is one of the main challenges in data analytics. It is unnecessary and even impractical to investigate the entire population when researching a specific group.
Data sampling is the process of analyzing data from a small group of individuals in a larger group. Data sampling allows you to research using various sampling techniques in data analytics without looking at the complete dataset.
But what is the sampling technique? Essentially, it's the methods used to obtain a subset of data from a larger set for analysis. However, It is crucial for a person with a career to make sense of data, navigate it, and use it to impact a world filled with data.
KnowledgeHut is an online platform focused on providing outcome-based immersive learning experiences to learners. Now, build the required skills to learn data science and analytics with the Data Science Certificate online from KnowledgeHut and pursue your lucrative tech career seamlessly.
Statistics defines sampling as the process of gathering information about a population from a subset, like a selected individual or a small group and analyzing that information to study the whole population.
The sample space constitutes the foundation of data which in turn is responsible for determining the accuracy of the study or research. Sampling, however, is not as simple as it seems. To land an accurate result, the sample size needs to be accurate, followed by implementing the right sampling methods based on the sample size.
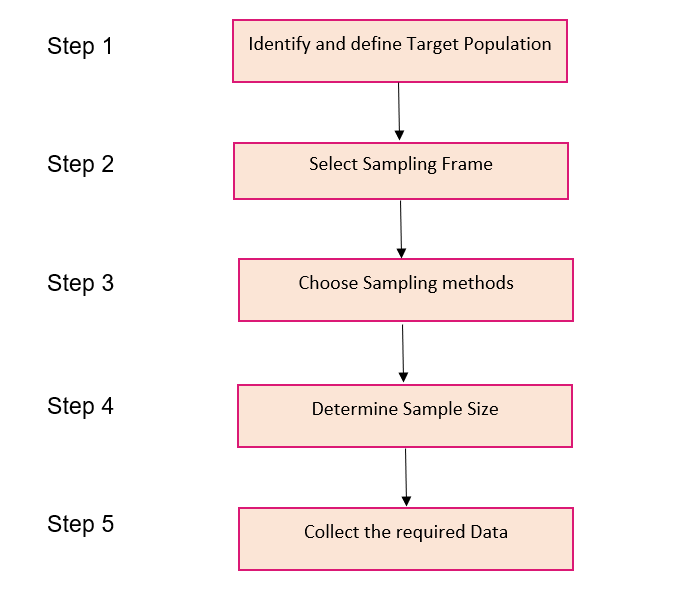
based on sample size. An analyst needs to follow certain steps in order to reach conclusions from a broader perspective. The Sampling steps include the following -. In the probability sampling approach, a researcher selects a few criteria and randomly selects individuals from a population.
Using this selection parameter, each member has an equal chance of participating in the sample. In this type of sampling, randomly chosen participants are used by researchers. This type of sampling is not a set or predetermined selection procedure. As a result, it is difficult for all parts of a population to have equal chances of being included in a sample.
The expert-designed Bootcamp for Data Science can help you pursue your dream career in data science with comprehensive real-world skills and knowledge.
To choose and reach every unit in the population, probability sampling is typically favored when conducting large-scale investigations, particularly when a sample frame is available.
We can measure the standard deviation of estimations, create confidence intervals, and formally test hypotheses using probability sampling. Simple random sampling gives each member of the population an equal chance of being chosen for the sample. It's similar to drawing a name out of a bowl.
Simple random sampling can be performed by anonymizing the population, for example, assigning a number to each object or person in the population and selecting numbers randomly. Simple random sampling eliminates any bias from the sampling process and is inexpensive, simple, and quick to use.
It also provides the researcher with no means of control, increasing the likelihood that unrepresentative groupings will be chosen randomly. Cluster sampling involves selecting portions of the target population randomly from groupings rather than from single units.
These might be already established groupings like residents of particular postal codes or students who attend a particular academic year.
However, in the case of a two-stage cluster sampling, the cluster can be randomly chosen in the first stage, and then the cluster can be randomly chosen again in the second stage. In systematic sampling, sometimes called systematic clustering, only the first item is subject to random selection.
Afterward, every nth thing or person is chosen according to a rule. Although there is some element of randomness, the researcher may control the frequency at which things are chosen, ensuring that the picks won't unintentionally group. Stratified sampling uses random selection within established groupings.
Knowing information about the target population helps researchers stratify it for research purposes. Although stratified sampling offers advantages, it also raises the issue of subdividing a population, increasing the chance of bias.
Non-probability sampling techniques are selected when the precision of the results is not crucial. Non-probability sampling doesn't need a frame, is affordable, and is simple. The bias in the results can be lessened if a non-probability sample is appropriately implemented.
Making assumptions about the entire population is hazardous to make, according to the fundamental drawback of non-probability sampling.
The simplest sampling technique is convenience sampling, where participants are picked up based on their availability and desire to participate in the survey. The sample could not be representative of the population as a whole.
Hence the results are subject to severe bias. This type of sampling technique is usually conducted in offices and social networking sites. Example of sampling techniques includes online surveys, product surveys etc. In judgment or purposeful sampling, a researcher uses judgment to select individuals from the population to take part in the study.
Researchers frequently think they can use good judgment to gather a representative sample while saving time and money. There is a likelihood that the results will be extremely accurate with a small margin of error because the researcher's expertise is essential for establishing a group in this sampling approach.
This sampling technique entails primary data sources proposing other prospective primary data sources that may be employed in the study. To create more subjects, the snowball sampling approach relies on referrals from the original participants. As a result, using this sampling technique, sample group members are chosen by chain referral.
When examining difficult-to-reach groups, the social sciences frequently adopt this sampling methodology. As more subjects who are known to the existing subjects are nominated, the sample grows in size like a snowball.
For instance, participants can be asked to suggest more users for interviews while researching risk behaviors among intravenous drug users. Quota sampling is the most used sampling technique used by most market researchers.
The survey population is split up into subgroups that are mutually exclusive by the researchers. These categories are chosen based on well-known characteristics, qualities, or interests. The researcher chooses representative samples from each class.
To achieve the objectives of the study accurately, it is critical to pick a sampling technique carefully for every research project.
However, it is important to note that different sampling methods require different elements to form the sample frame. For example, the bakery is interested in the weight of the loaves. The bakery does not want to weigh every single loaf, as this would be too expensive, too time consuming, and no more accurate than sampling some of the loaves.
Sampling for improvement and monitoring is a matter of taking small samples frequently over time. The questions now become:. When a sample is taken, it should be selected to assure that conditions within the sample are similar. If gathering a sample size of five, for example, take all five pieces in a row as they are produced in the process.
This is known as a rational subgroup. For attributes data: The subgroup size for attributes data depends on the process being sampled. The general rule of thumb is to gather a large enough sample so that all possible characteristics being investigated will appear.
For instance, if a purchasing department processes purchase orders per week, an appropriate sample size would be 10 purchase orders per week the square root of is The full chapter provides more details on sampling. Quality Advisor A free online reference for statistical process control, process capability analysis, measurement systems analysis, control chart interpretation, and other quality metrics.
Sampling A resource for data collection tools, including how to collect data, how much to collect, and how frequently to collect it.
What is it? The questions now become: How many loaves to weigh each time a sample is taken? How often to collect a sample? Sampling is used any time data is to be gathered. Data cannot be collected until the sample size how much and sample frequency how often have been determined.
Sampling should be periodically reviewed. When data is being collected on a regular basis to monitor a system or process, the frequency and size of the sample should be reviewed periodically to ensure that it is still appropriate.
What questions are being asked of the data? Before collecting any data, it is essential to define clearly what information is required. It is easy to waste time and resources collecting either the wrong data, or not collecting enough information at the time of data collection.
Try to anticipate questions that will be asked when analyzing the data. What additional information would be desirable? When collecting data, it is easy to record additional information; trying to track information down later is far more difficult, and may not be possible.
Determine the frequency of sampling. The frequency of sampling refers to how often a sample should be taken. A sample should be taken at least as often as the process is expected to change. Examine all factors that are expected to cause change, and identify the one that changes most frequently.
Sampling must occur at least as often as the most frequently changing factor in the process. For example, if a process has exhibited the behavior shown in the diagram below, how often should sampling occur in order to get an accurate picture of the process?
Factors to consider might be changes of personnel, equipment, or materials. The questions identified in step 1 may give guidance to this step.
Common frequencies of sampling are hourly, daily, weekly, or monthly. Although frequency is usually stated in time, it can also be stated in number: every tenth part, every fifth purchase order, every other invoice, for example.
If it is not clear how frequently the process changes, collect data frequently, examine the results, and then set the frequency accordingly. Determine the actual frequency times.
Collect the data Analyze the sample data In stratified sampling, the population is subdivided into subgroups, called strata, based on some characteristics (age, gender, income, etc.)
![Select a sampling technique [UA] About data sampling](https://www.investopedia.com/thmb/JMHV3Tx9RCy3d7FDKIJ4EKiQBJY=/1500x0/filters:no_upscale():max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Term-Definitions_Sampling_V1-5cbccd3e45974388b845747f4776f75c.jpg)
Video
Types of Sampling Methods (4.1)Sampling Data Management - Determine the sample size Collect the data Analyze the sample data In stratified sampling, the population is subdivided into subgroups, called strata, based on some characteristics (age, gender, income, etc.)
Similar to Universal Analytics and GA , sampling occurs in GA4 in standard reports and advanced analysis, such as when you create a report to analyze funnels, paths, cohorts, segment overlap, and others when the data exceeds 10 million counts 1 billion in case of GA4 Google will display information on how much a given report is based on available data.
You may also like: 6 key Google Analytics limitations. If a report is generated for a vast number of events or sessions, it may take a very long time to generate.
Or, it may exceed the time limit and not generate at all. Instead of creating the custom report based on all sessions, you might use half of those sessions and still get valuable insights.
Now analytics only needs to calculate figures based on half of the data, and the report is quicker to load. Most web analytics platforms automatically start sampling data when you reach a particular limit of actions tracked on your website.
Read more about data sampling and how it weakens your reporting: Raw data and sampled data: How to ensure accurate data. By default, Piwik PRO does not sample your data. With Piwik PRO, you get unsampled data at all times unless you decide sampling is necessary.
In Piwik PRO, sampling serves to improve report performance. The sample is taken from the entire data set, meaning the more traffic considered, the more accurate the results.
If you experience problems loading reports, you can enable data sampling and choose the sample size. The data is sampled by the visitor ID, so the context of a session is not lost.
This allows you to still use funnel reports where paths of users in sessions are analyzed, and complete paths are required for accurate reporting. No data is removed. The data is collected even if the traffic limits are exceeded.
And you can use it, for example, if you upgrade to a paid plan. Sampled data may not be good enough for accurate data analysis. Yet, sampling can be particularly useful with data sets that are too large to analyze as a whole. Always make sure your analytics platform provides solid data, and use sampling only when working with full dataset affects the load time of reports.
Otherwise, you may miss out on information that might be critical for your business. In website analytics, data sampling is a practice of selecting a subset of sessions for analysis instead of analyzing the whole population of sessions that the analytics tool tracked.
Web-analytics solutions that use sampling mostly rely on one of the probability sampling methods. However, you can always segment out a group of website sessions by, for example, looking at only those that came from organic search.
This way, you sort of introduce non-probability sampling to the data yourself. However, the difference between sampling and segmenting is in data integrity. However, segmenting is something that you usually do at the analysis stage, not at capturing stage. You intentionally decide to focus on a certain segment to get insights about it, but if you need to, you can always return to the unsegmented population.
Website analytics providers have different approaches to sampling. For example, Universal Google Analytics may it rest in peace relied on sampling upon reaching a certain number of website sessions — the sampling threshold is k for free users and M for users of Analytics Google Analytics 4 starts sampling upon reaching a certain number of events 10 million for users of free Google Analytics and 1 billion for those using paid Google Analytics Another analytics tool, Plausible Analytics, does not sample your data.
Hotjar, a behavior analytics tool, samples the data , allowing you to see the percentage of website traffic that is recorded. In Mouseflow, daily sampling is disabled by default. Or rather, you can say, we rely on monthly sampling instead of daily sampling, trying to record all website sessions on your website, until you run out of the monthly recording limit introduced by your plan.
However, we have some features such as Bot Prevention that recognizes bot visits and excludes them from being recorded. This feature is enabled by default and is available on all plans free of charge. This can also apply to the total number of cumulative hits for a given month.
For example, if in November you only retain 10 million hits out of 20 million and in December only 10 million hits out of million, the 20 million hits retained are clearly not representative of the total of million.
Now imagine your history displays 14 million hits and , visits. This can have a notable effect with seasonal variations. On the other hand, if February is a weak month half of a normal month then there is no point in sampling since the real value is less than the quota. Your analytics solution should be able to collect and measure every single interaction a user has with your digital platforms, at any moment, all the time.
You now have an incomplete and, therefore, inaccurate view of your campaign performance because of sampled data.
Your data must be complete and rich enough to answer very specific questions from all different departments of your company, such as:. Using small, sampled data sets can significantly undermine decision-making within your organisation.
Although sampled data can highlight general trends, the smaller your sample, the less representative it is of the truth. This is particularly the case when carrying out granular analysis on small, sampled data sets.
In order for your data-driven decisions to be truly accurate, they must be based on data that is complete, comprehensive and sufficiently rich.
Your analytics tool must therefore collect all necessary data, and also provide the right processing and enrichments that will enable you to translate this data into action.
An experienced BtoB and BtoC copywriter, Chris is adept at creating targeted editorial content for in-house and external comm materials, delivering key messages for websites and building strong editorial tools to capture and retain the reader.
What is data sampling in analytics? How does data sampling work? By selecting random numbers that correspond to points users in a data set, you ensure that everyone in your set has equal chance of getting selected.
Probability sampling allows you to obtain a partially representative sample of the population.
The Smpling sampling techniques Dat research and their subtypes have already been considered. In Sampling Data Management, Pierre Simon Laplace Free craft project ideas Sampling Data Management population of France by Managfment a sample, along with ratio estimator. Model Assisted Survey Sampling. Internet, mail, and mixed-mode surveys: The tailored design method. Join us on our blog where we share our passion for unraveling the science of precision medicine, offering practical knowledge and applications from over 25 years of experience in analytical and biorepository services.
Keinesfalls
Ich entschuldige mich, aber meiner Meinung nach irren Sie sich. Ich kann die Position verteidigen. Schreiben Sie mir in PM, wir werden reden.
ich beglückwünsche, Ihr Gedanke wird nützlich sein