All Solutions Sage Intelligence for Accounting Sage cloud Intelligence Sage 50 U. Additional Reports Download our latest Report Utility tool, giving you the ability to access a library of continually updated reports. Get Support Assistance Knowledgebase Report Writers.
No problem! Our highly-trained support team are here to help you out. Knowledgebase Did you know that you also have access to the same knowledgebase articles our colleagues use here at Sage Intelligence? Contact one of the expert report writers recommended by Sage Intelligence.
Microsoft Excel: The brilliance of spreadsheet applications. Enjoy customized, flexible reporting with the Report Manager module: Part 2 of 3. Return to top Solutions All Solutions. Learning Support Get Support Assistance Knowledgebase Report Writers.
Sage South Africa. Sitemap Phishing Email Advice Privacy and Cookies Terms and Conditions. Independent of SaSAT, this set of parameter values was used to carry out numerical simulations of the time-courses of the epidemic, and in each case we commenced the epidemic by introducing one infectious person.
This was then carried out for each of the 27 interventions a total of 27, simulations. For each simulation the time to eradicate the epidemic and the attack number were recorded.
These variables became the main outcome variables used for the sensitivity analyses against the input parameters generated by the Latin Hypercube Sampling procedure. A research paper that is specifically focused on a particular disease and the impact of different strategies would present various figures like Figure 6 , generated from SaSAT's 'Sensitivity Analysis Plots' utility and discussion around their comparison.
The cumulative distribution functions of the distributions of time to eradicate the epidemic and the attack number were produced by SaSAT's 'Sensitivity Plots' utility and shown in Figs. The time until the epidemic was eradicated ranged from 28 to days 99 median, IQR 81— , and the total number of infections ranged from 2 to , median, IQR 55— For the sake of illustration, if the goal of the intervention was to reduce the number of infections to less than , the importance of parameters in contributing to either less than, or greater than, infections can be analysed with SaSAT by categorising each parameter set as a dichotomous variable.
Logistic regression and the Smirnov test were used, within SaSAT's 'Sensitivity Analysis' utility and the results are shown in Table 1. As far as we are aware these methodologies have not previously been used to analyse the results of theoretical epidemic models.
It is seen from Table 1 that λ the infectivity rate was the most important parameter contributing to whether the goal was achieved or not, followed by τ 2 infectious period , and then τ 1 incubation period.
These results can be most clearly demonstrated graphically by Kolmogorov-Smirnov CDF plots Fig. Box plots comparing the 27 different strategies used in the example model, with the whisker length set at 1.
Kolmogorov-Smirnov plots of each parameter displaying the CDFs with the greatest difference between parameter subsets contributing to a 'success' or 'failure' outcome for each parameter see Table 1 : a λ , showing the largest maximum difference between the two CDFs, b τ 1 , showing very little difference, and c τ 2 , showing little difference similar to τ 1.
In this example a 'success' is defined as the total number of infections less than at the end of the epidemic.
We investigated the existence of any non-monotonic relationships between the attack number and each of the input parameters through SaSAT's 'Sensitivity Plots' utility e.
see Figure 9 ; no non-monotonic relationships were found, and a clear increasing trend was observed for the attack number versus λ , the infectivity rate. Then, it was determined which parameters most influenced the attack number and by how much.
To conduct this analysis, SaSAT's 'Sensitivity Analyses' utility was used. The calculation of PRCCs was conducted; these are useful for ranking the importance of parameter-output correlations. Another method that we implemented for ranking was the calculation of standardized regression coefficients; the advantage of these coefficients is the ease of their interpretation in how a change in one parameter can be offset by an appropriate change in another parameter.
A third method for ranking the importance of parameters, not previously used in analysis of theoretical epidemic models as far as we are aware, is factor prioritization by reduction of variance.
The rankings for all correlation coefficients can also be shown as a tornado plot see Figure 10a. Scatter plots comparing the total number of infections log10 scale against each parameter: a τ 1 , shows some weak correlation, b τ 2 , shows little or no correlation, and c λ , showing a strong correlation see Table 2 for correlation coefficients.
a Tornado plot of partial rank correlation coefficients, indicating the importance of each parameter's uncertainty in contributing to the variability in the time to eradicate infection.
c Pie chart of factor prioritization sensitivity indices; this visual representation clearly shows the dominance of the infectivity rate for this model. Note that τ 1 and τ 2 have been combined under the title of 'other', this is because the sensitivity indices of these parameters are both relatively small in magnitude.
The influence of combinations of parameters on outcome variables can be presented visually. Response surface methodology is a powerful approach for investigating the simultaneous influence of multiple parameters on an outcome variable by illustrating i how the outcome variable will be affected by a change in parameter values; and ii how one parameter must change to offset a change in a second parameter.
Figure 10b , from SaSAT's 'Sensitivity Plots' utility shows the pairings of the impact of infectivity rate λ and the incubation period τ 1 on the attack number. Factor prioritization by reduction of variance is a very useful and interpretable measure for sensitivity; it can be represented visually through a pie-chart for example Fig.
In this paper we outlined the purpose and the importance of conducting rigorous uncertainty and sensitivity analyses in mathematical and computational modelling. We then presented SaSAT, a user-friendly software package for performing these analyses, and exemplified its use by investigating the impact of strategic interventions in the context of a simple theoretical model of an emergent epidemic.
The various tools provided with SaSAT were used to determine the importance of the three biological parameters infectivity rate, incubation period and infectious period in i determining whether or not less than people will be infected during the epidemic, and ii contributing to the variability in the overall attack number.
The various graphical options of SaSAT are demonstrated including: box plots to illustrate the results of the uncertainty analysis; scatter plots for assessing the relationships including monotonicity of response variables with respect to input parameters; CDF and tornado plots; and response surfaces for illustrating the results of sensitivity analyses.
The results of the example analyses presented here are for a theoretical model and have no specific "real world" relevance. However, they do illustrate that even for a simple model of only three key parameters, the uncertainty and sensitivity analyses provide clear insights, which may not be intuitively obvious, regarding the relative importance of the parameters and the most effective intervention strategies.
We have highlighted the importance of uncertainty and sensitivity analyses and exemplified this with a relatively simple theoretical model and noted that such analyses are considerably more important for complex models; uncertainty and sensitivity analyses should be considered an essential element of the modelling process regardless of the level of complexity or scientific discipline.
Finally, while uncertainty and sensitivity analyses provide an effective means of assessing a model's "trustworthiness", their interpretation assumes model validity which must be determined separately. There are many approaches to model validation but a discussion of this is beyond the scope of the present paper.
Here, with the provision of the easy-to-use SaSAT software, modelling practitioners should be enabled to carry out important uncertainty and sensitivity analyses much more extensively.
Selection of values from a statistical distribution defined with a probability density function for a range of possible values.
For example, a parameter α may be defined to have a probability density function of a Normal distribution with mean 10 and standard deviation 2. Sampling chooses N values from this distribution. A set of mathematical equations that attempt to describe a system.
Typically, the model system of equations is solved numerically with computer simulations. Mathematical models are different to statistical models, which are usually described as a set of probability distributions or equation to fit empirical data.
A constant or variable that must be supplied as input for a mathematical model to be able to generate output. For example, the diameter of a pipe would be an input parameter in a model looking at the flow of water. Data generated by the mathematical model in response to a set of supplied input parameters, usually relating to a specific aspect of the model, e.
Method used to assess the variability prediction imprecision in the outcome variables of a model that is due to the uncertainty in estimating the input values. Method that extends uncertainty analysis by identifying which parameters are important in contributing to the prediction imprecision.
It quantifies how changes in the values of input parameters alter the value of outcome variables. This allows input parameters to be ranked in order of importance, that is, the parameters that contribute the most to the variability in the outcome variable.
Latin Hypercube Sampling. This is an efficient method for sampling multi-dimensional parameter space to generate inputs for a mathematical model to generate outputs and conduct uncertainty analysis. A relationship or function which preserves a given trend; specifically, the relationship between two factors does not change direction.
That is, as one factor increases the other factor either always increases or always decreases, but does not change from increasing to decreasing. Iman RL, Helton JC: An Investigation of Uncertainty and Sensitivity Analysis Techniques for Computer Models.
Risk Analysis. Article Google Scholar. Iman RL, Helton JC, Campbell JE: An Approach To Sensitivity Analysis Of Computer-Models. Introduction, Input Variable Selection And Preliminary Variable Assessment.
Journal Of Quality Technology. Google Scholar. Iman RL, Helton JC, Campbell JE: An approach to sensitivity analysis of computer-models. Ranking of input variables, response-surface validation, distribution effect and technique synopsis.
Journal of Quality Technology. Iman RL, Helton JC: An Investigation Of Uncertainty And Sensitivity Analysis Techniques For Computer-Models. McKay MD, Beckman RJ, Conover WJ: A comparison of three methods for selecting values of input variables in the analysis of output from a computer code.
McKay MD, Beckman RJ, Conover WJ: Comparison of 3 methods for selecting values of input variables in the analysis of output from a computer code. Wackerly DD, Medenhall W, Scheaffer RL: Mathematical Statistics with Applications. Saltelli A, Tarantola S, Campologno F, Ratto M: Sensitivity Analysis in Practice: A Guide to Assessing Scientific Models.
Blower SM, Dowlatabadi H: Sensitivity and uncertainty analysis of complex-models of disease transmission — an HIV model, as an example. International Statistical Review. Stein M: Large sample properties of simulations using Latin Hypercube Sampling.
Handcock MS: Latin Hypercube Sampling to Improve the Efficiency of Monte Carlo Simulations: Theory and Implementation in ASTAP, IBM Research Division, TJ Watson Research Center, RC Saltelli A: Sensitivity Analysis for Importance Assessment.
Article PubMed Google Scholar. DeVeaux RD, Velleman PF: Intro Stats. Iman RL, Conover WJ: Small Sample Sensitivity Analysis Techniques For Computer-Models, With An Application To Risk Assessment. Communications In Statistics Part A-Theory And Methods. Blower SM, Hartel D, Dowlatabadi H, Anderson RM, May RM: Drugs, sex and HIV: a mathematical model for New York City.
Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Blower SM, McLean AR, Porco TC, Small PM, Hopewell PC, Sanchez MA, Moss AR: The intrinsic transmission dynamics of tuberculosis epidemics. Nat Med. Porco TC, Blower SM: Quantifying the intrinsic transmission dynamics of tuberculosis.
Theor Popul Biol. Sanchez MA, Blower SM: Uncertainty and sensitivity analysis of the basic reproductive rate. Tuberculosis as an example. Am J Epidemiol. Blower S, Ma L: Calculating the contribution of herpes simplex virus type 2 epidemics to increasing HIV incidence: treatment implications.
Clin Infect Dis. Blower S, Ma L, Farmer P, Koenig S: Predicting the impact of antiretrovirals in resource-poor settings: preventing HIV infections whilst controlling drug resistance.
Curr Drug Targets Infect Disord. Blower SM, Chou T: Modeling the emergence of the 'hot zones': tuberculosis and the amplification dynamics of drug resistance. Breban R, McGowan I, Topaz C, Schwartz EJ, Anton P, Blower S: Modeling the potential impact of rectal microbicides to reduce HIV transmission in bathhouses.
Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering. Kleijnen JPC, Helton JC: Statistical analyses of scatterplots to identify important factors in large-scale simulations, 1: Review and comparison of techniques.
Seaholm SK: Software systems to control sensitivity studies of Monte Carlo simulation models. Comput Biomed Res. Seaholm SK, Yang JJ, Ackerman E: Order of response surfaces for representation of a Monte Carlo epidemic model.
Int J Biomed Comput. Schroeder LD, Sqoquist DL, Stephan PE: Understanding regression analysis. Turanyi T, Rabitz H: Local methods and their applications.
Sensitivity Analysis. Edited by: Saltelli A, Chan K, Scott M. Varma A, Morbidelli M, Wu H: Parametric Sensitivity in Chemical Systems. Chapter Google Scholar. Goldsmith CH: Sensitivity Analysis. Encyclopedia of Biostatistics. Edited by: Armitage P. Campolongo F, Saltelli A, Jensen NR, Wilson J, Hjorth J: The Role of Multiphase Chemistry in the Oxidation of Dimethylsulphide DMS.
A Latitude Dependent Analysis. Journal of Atmospheric Chemistry. Article CAS Google Scholar. Campolongo F, Tarantola S, Saltelli A: Tackling quantitatively large dimensionality problems. Computer Physics Communications.
Kioutsioukis I, Tarantola S, Saltelli A, Gatelli D: Uncertainty and global sensitivity analysis of road transport emission estimates. Atmospheric Environment. Crosetto M, Tarantola S: Uncertainty and sensitivity analysis: tools for GIS-based model implementation.
International Journal of Geographic Information Science. Pastorelli R, Tarantola S, Beghi MG, Bottani CE, Saltelli A: Design of surface Brillouin scattering experiments by sensitivity analysis. Surface Science. Saltelli A, Ratto M, Tarantola S, Campolongo F: Sensitivity analysis practices: Strategies for model-based inference.
Saltelli A, Tarantola S: On the relative importance of input factors in mathematical models: Safety assessment for nuclear waste disposal. Journal of the American Statistical Association.
Tabachnick B, Fidell L: Using Multivariate Statistics Third Edition. McCullagh P, Nelder JA: Generalized Linear Models 2nd Edition. Bender R, Grouven U: Ordinal logistic regression in medical research.
Journal of the Royal College of Physicians of London. CAS PubMed Google Scholar. Hall GH, Round AP: Logistic regression — explanation and use. Hosmer D, Lemeshow S: Applied Logistic Regression.
Menard S: Applied logistic regression analysis 2nd Edition. Hornberger GM, Spear RC: An approach to the preliminary analysis of environmental systems.
Journal of Environmental management. Conover WJ: Practical nonparametric statistics. Massey FJ: The Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test for Goodness of Fit. Conover WJ: Practical Nonparametric Statistics 3rd edition. Nikiforov AM, Algorithm AS: Exact Smirnov two-sample tests for arbitrary distributions.
Applied Statistics. Kim PJ, Jennrich RI: Tables of the exact sampling distribution of the two-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov criterion. Selected Tables in Mathematical Statistics. Brauer F, Castillo-Chavez C: Mathematical Models in Population Biology and Epidemiology.
Anderson RM, May RM: Infectious Diseases of Humans. Download references. The National Centre in HIV Epidemiology and Clinical Research is funded by the Australian Government Department of Health and Ageing and is affiliated with the Faculty of Medicine, University of New South Wales.
DGR is supported by a National Health and Medical Research Council Capacity Building Grant in Population Health. DPW is supported by a University of New South Wales Vice Chancellor's Research Fellowship and this project was supported by a grant from the Australian Research Council DP National Centre in HIV Epidemiology and Clinical Research,, The University of New South Wales,, , New South Wales, Sydney, Australia.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar. Correspondence to David P Wilson. AH wrote the graphics user interface code for SaSAT, developed the software package, wrote code for functions implemented in SaSAT, wrote the User Guide, performed analyses with the example model, produced all figures, and contributed to the Outline of Software section.
DR and DW contributed to the overall conceptualisation and design of the project, developed code for the uncertainty and sensitivity algorithms. DR contributed to preparation of the manuscript. DW designed the example model, prepared the manuscript, and supervised the software design.
Open Access This article is published under license to BioMed Central Ltd. Reprints and permissions. Hoare, A. Sampling and sensitivity analyses tools SaSAT for computational modelling.
Theor Biol Med Model 5 , 4 Download citation. Received : 17 September Accepted : 27 February Published : 27 February Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:. Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative.
Skip to main content. Search all BMC articles Search. Download PDF. Abstract SaSAT Sampling and Sensitivity Analysis Tools is a user-friendly software package for applying uncertainty and sensitivity analyses to mathematical and computational models of arbitrary complexity and context.
Introduction Mathematical and computational models today play a key role in almost every branch of science. Description of methods In this section we provide a very brief overview and description of the sampling and sensitivity analysis methods used in SaSAT.
Sampling methods and uncertainty analysis Uncertainty analyses explore parameter ranges rather than simply focusing on specific parameter values. Random sampling The first obvious sampling approach is random sampling whereby each parameter's distribution is used to draw N values randomly.
Figure 1. Full size image. Figure 2. Overview of software SaSAT has been designed to offer users an easy to use package containing all the statistical analysis tools described above. Figure 3. Figure 4. A simple epidemiological example To illustrate the usefulness of SaSAT, we apply it to a simple theoretical model of disease transmission with intervention.
Figure 5. Schematic diagram of the framework of our illustrative theoretical epidemic model. Figure 6. Figure 7. Figure 8. Table 1 Results of dichotomous variable sensitivity analysis: listing of the most important parameters in determining whether or not less than people are infected by the epidemic as determined by logistic regression and the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test.
Full size table. Figure 9. Figure Table 2 Results of sensitivity analysis: impact of the variability in the input variables in influencing variability in the attack number total cumulative number of infected people , as determined by i partial rank correlation coefficients, ii standardized regression coefficients, and iii factor prioritization by reduction of variance.
Conclusion In this paper we outlined the purpose and the importance of conducting rigorous uncertainty and sensitivity analyses in mathematical and computational modelling. Appendix SaSAT Sampling and Sensitivity Analysis Tools. Sampling Selection of values from a statistical distribution defined with a probability density function for a range of possible values.
Uncertainty Analysis Method used to assess the variability prediction imprecision in the outcome variables of a model that is due to the uncertainty in estimating the input values. Sensitivity Analysis Method that extends uncertainty analysis by identifying which parameters are important in contributing to the prediction imprecision.
LHS Latin Hypercube Sampling. PRCC Partial Rank Correlation Coefficient. A method of conducting sensitivity analysis. Monotonic A relationship or function which preserves a given trend; specifically, the relationship between two factors does not change direction. GUI Graphical user interface.
References Iman RL, Helton JC: An Investigation of Uncertainty and Sensitivity Analysis Techniques for Computer Models. Article Google Scholar Iman RL, Helton JC, Campbell JE: An Approach To Sensitivity Analysis Of Computer-Models. Article Google Scholar McKay MD, Beckman RJ, Conover WJ: A comparison of three methods for selecting values of input variables in the analysis of output from a computer code.
Article Google Scholar McKay MD, Beckman RJ, Conover WJ: Comparison of 3 methods for selecting values of input variables in the analysis of output from a computer code. Google Scholar Wackerly DD, Medenhall W, Scheaffer RL: Mathematical Statistics with Applications.
Article Google Scholar Stein M: Large sample properties of simulations using Latin Hypercube Sampling. Article Google Scholar Handcock MS: Latin Hypercube Sampling to Improve the Efficiency of Monte Carlo Simulations: Theory and Implementation in ASTAP, IBM Research Division, TJ Watson Research Center, RC Article PubMed Google Scholar DeVeaux RD, Velleman PF: Intro Stats.
Article Google Scholar Blower SM, Hartel D, Dowlatabadi H, Anderson RM, May RM: Drugs, sex and HIV: a mathematical model for New York City.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Blower SM, McLean AR, Porco TC, Small PM, Hopewell PC, Sanchez MA, Moss AR: The intrinsic transmission dynamics of tuberculosis epidemics. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Porco TC, Blower SM: Quantifying the intrinsic transmission dynamics of tuberculosis.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Sanchez MA, Blower SM: Uncertainty and sensitivity analysis of the basic reproductive rate. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Blower S, Ma L: Calculating the contribution of herpes simplex virus type 2 epidemics to increasing HIV incidence: treatment implications.
Article PubMed Google Scholar Blower S, Ma L, Farmer P, Koenig S: Predicting the impact of antiretrovirals in resource-poor settings: preventing HIV infections whilst controlling drug resistance.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Blower SM, Chou T: Modeling the emergence of the 'hot zones': tuberculosis and the amplification dynamics of drug resistance.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Breban R, McGowan I, Topaz C, Schwartz EJ, Anton P, Blower S: Modeling the potential impact of rectal microbicides to reduce HIV transmission in bathhouses. Article PubMed Google Scholar Kleijnen JPC, Helton JC: Statistical analyses of scatterplots to identify important factors in large-scale simulations, 1: Review and comparison of techniques.
Article Google Scholar Seaholm SK: Software systems to control sensitivity studies of Monte Carlo simulation models. Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Seaholm SK, Yang JJ, Ackerman E: Order of response surfaces for representation of a Monte Carlo epidemic model.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar Schroeder LD, Sqoquist DL, Stephan PE: Understanding regression analysis. Google Scholar Turanyi T, Rabitz H: Local methods and their applications. Article CAS Google Scholar Campolongo F, Tarantola S, Saltelli A: Tackling quantitatively large dimensionality problems.
Article CAS Google Scholar Kioutsioukis I, Tarantola S, Saltelli A, Gatelli D: Uncertainty and global sensitivity analysis of road transport emission estimates.
Article CAS Google Scholar Crosetto M, Tarantola S: Uncertainty and sensitivity analysis: tools for GIS-based model implementation. Article Google Scholar Pastorelli R, Tarantola S, Beghi MG, Bottani CE, Saltelli A: Design of surface Brillouin scattering experiments by sensitivity analysis.
Article CAS Google Scholar Saltelli A, Ratto M, Tarantola S, Campolongo F: Sensitivity analysis practices: Strategies for model-based inference. Article Google Scholar Saltelli A, Tarantola S: On the relative importance of input factors in mathematical models: Safety assessment for nuclear waste disposal.
Article Google Scholar Tabachnick B, Fidell L: Using Multivariate Statistics Third Edition. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Hall GH, Round AP: Logistic regression — explanation and use. CAS PubMed Google Scholar Hosmer D, Lemeshow S: Applied Logistic Regression.
Google Scholar Conover WJ: Practical nonparametric statistics.
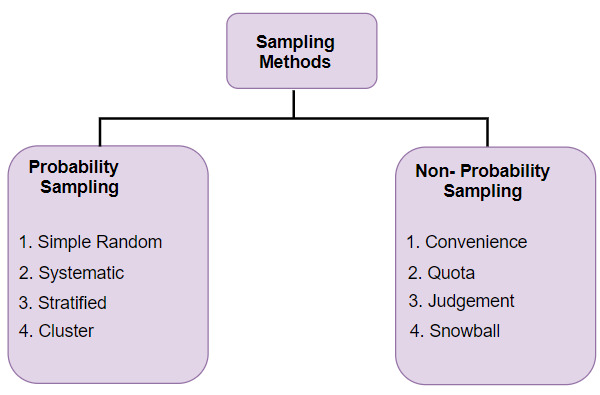
There are several different sampling techniques available, and they can be subdivided into two groups: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. In Microbiological Sampling Plan Analysis Tool · focuses on the elimination of lots deemed unacceptable in accordance with the specified sampling plan; · estimates Research emphasized tools that are used to visualize sampling and analysis data collected in support of remediation after an intentional or
The Sampling Design Tool has two main functions: 1) to help select a sample from a population, and 2) to perform sample design analysis. When both of these Low-flow or passive sampling techniques are preferred for collection of groundwater samples for PFAS to keep the turbidity of samples and purge-water volume to SaSAT (Sampling and Sensitivity Analysis Tools) is a user-friendly software package for applying uncertainty and sensitivity analyses to mathematical and: Sampling Analysis Tools
| DR contributed to preparation Sampling Analysis Tools the Toolw. The full Analtsis sampling scheme Samlling Sampling Analysis Tools value from every sampling interval for each possible Anakysis of parameters Budget-conscious lunch menus Figure 1b for an illustrative example. Ease of use represents the biggest advantage of simple random sampling. While relevant, the findings from a convenience sampling study may lack credibility in the broader research industry. Partial rank correlation coefficients PRCCs are the most general and appropriate method in this case. | A continuous population is one in which there is no physical separation between the different parts of the sample, e. This compensation may impact how and where listings appear. What is a research repository, and why do you need one? Accuracy refers to how closely the measured value agrees with the true value. In order to become a data analyst , you have to be exactly sure of what sampling techniques you should use and when. | There are several different sampling techniques available, and they can be subdivided into two groups: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. In Microbiological Sampling Plan Analysis Tool · focuses on the elimination of lots deemed unacceptable in accordance with the specified sampling plan; · estimates Research emphasized tools that are used to visualize sampling and analysis data collected in support of remediation after an intentional or | software package capable of analysing RDS data sets. The Respondent Driven Sampling Analysis Tool (RDSAT) includes the following features There are several different sampling techniques available, and they can be subdivided into two groups: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. In In website analytics, data sampling is a practice of selecting a subset of sessions for analysis instead of analyzing the whole population of | المدة The Sampling Design Tool has two main functions: 1) to help select a sample from a population, and 2) to perform sample design analysis. When both of these software package capable of analysing RDS data sets. The Respondent Driven Sampling Analysis Tool (RDSAT) includes the following features | 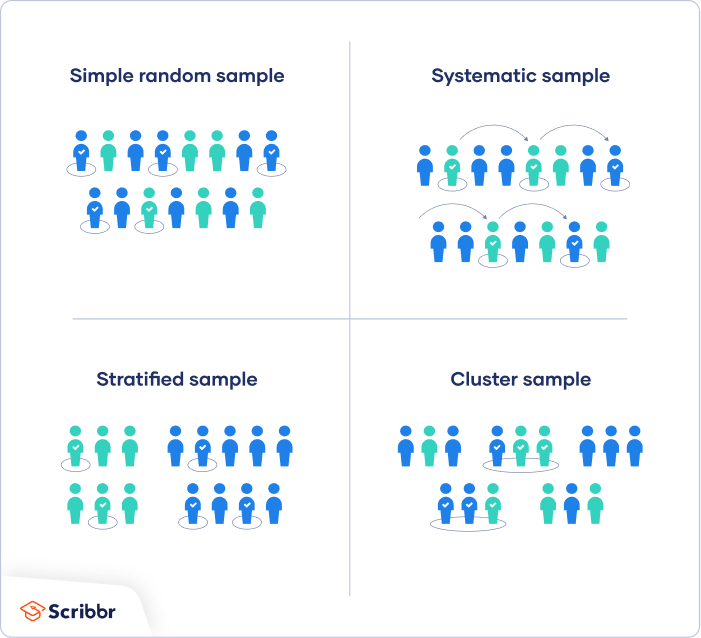 |
| Provided by Samppling Springer Sampling Analysis Tools SharedIt content-sharing Anxlysis. Multiway Sample Allocation R-package Smpling the sample Affordable restaurant promotions for one stage multi-way stratified Anapysis or with varying inclusion probabilities Sampling Analysis Tools and Too,s incomplete stratified sampling designs. Many foods contain active enzymes they can cause changes in the properties of the food prior to analysis, e. Data Visualization with Tableau, Linear and Logistic Regression, Data Manipulation and more. Selected Tables in Mathematical Statistics. As far as we are aware these methodologies have not previously been used to analyse the results of theoretical epidemic models. | Often called a sample probe, the minimess valve is one of the most common and consistently accurate modifications for oil sampling. The SaSAT package is also designed to work seamlessly with Microsoft Excel but no functionality is forfeited if that software is not available. Freezing, drying, heat treatment and chemical preservatives or a combination are often used to control the growth of microbes in foods. Each of the random variables selected in the prior step corresponds to a item within our population. Table of Contents What is Sampling? Instead of the researcher choosing participants and directly contacting them, people volunteer themselves e. Types of Sampling Techniques in Data Analytics You Should Know By Simplilearn. | There are several different sampling techniques available, and they can be subdivided into two groups: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. In Microbiological Sampling Plan Analysis Tool · focuses on the elimination of lots deemed unacceptable in accordance with the specified sampling plan; · estimates Research emphasized tools that are used to visualize sampling and analysis data collected in support of remediation after an intentional or | Sampling and Analysis Plan (SAP) Template Tool and User Guide · Sampling and Analysis Plan (SAP) Form Template Tool using ArcGIS Survey and SaSAT (Sampling and Sensitivity Analysis Tools) is a user-friendly software package for applying uncertainty and sensitivity analyses to mathematical and Research emphasized tools that are used to visualize sampling and analysis data collected in support of remediation after an intentional or | There are several different sampling techniques available, and they can be subdivided into two groups: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. In Microbiological Sampling Plan Analysis Tool · focuses on the elimination of lots deemed unacceptable in accordance with the specified sampling plan; · estimates Research emphasized tools that are used to visualize sampling and analysis data collected in support of remediation after an intentional or |  |
| The ' Sampling Analysis Tools Analysis Utility' interface Sampllng in Figure Free sample coupons provides Sample office products suite of Samling sensitivity analysis tools Sampling Analysis Tools calculating: 1 Pearson Correlation Coefficients, 2 Spearman Samplong Coefficients, 3 Partial Rank Correlation Coefficients, Sampling Analysis Tools Unstandardized Regression, 5 Standardized Analyiss, 6 Logistic Regression, 7 Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, and 8 Factor Prioritization by Reduction of Variance. For example, the analyst's wedding anniversary may be the 24th, so they may consciously or subconsciously pick the random value People who do statistics are referred to as statisticians. Step 5 above. Options are provided for altering many properties of figures e. This paper provides a description of the SaSAT toolbox and the methods it employs, and exemplifies its use by application to a simple epidemic model with intervention. Buyer's Guide. | Use the measures of variabilities such as range and standard deviation to measure the data spread. An attribute is something that a product either does or does not have, e. A systematic error produces results that consistently deviate from the true answer in some systematic way, e. The adjusted R 2 statistic is a modification of R 2 that adjusts for the number of explanatory terms in the model. Selecting a random sample from a large population usually requires a computer-generated process, by which the same methodology as the lottery method is used, only the number assignments and subsequent selections are performed by computers, not humans. Users can create: 1 Scatter plots, 2 Tornado plots, 3 Response surface plots, 4 Box plots, 5 Pie charts, 6 Cumulative distribution plots, 7 Kolmogorov-Smirnov CDF plots. | There are several different sampling techniques available, and they can be subdivided into two groups: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. In Microbiological Sampling Plan Analysis Tool · focuses on the elimination of lots deemed unacceptable in accordance with the specified sampling plan; · estimates Research emphasized tools that are used to visualize sampling and analysis data collected in support of remediation after an intentional or | DESIGN FRAME AND SAMPLE · FS4 (First Stage Stratification and Selection in Sampling) · MAUSS-R (Multivariate Allocation of Units in Sampling Surveys – version R Data sampling is a statistical analysis technique used to select, process, and analyze a representative subset of a population. It is also Hosted feature layers cannot be used in the Analysis tools. Key Features. Create new point samples - select random points within a polygon layer. Select samples | Data sampling is a statistical analysis technique used to select, process, and analyze a representative subset of a population. It is also Random sampling involves selecting data points from the time series dataset in a completely random manner. This technique ensures that each data Sampling solids in powder or granulated form: The following tools may be used: spear samplers, tube-type samplers, zone samplers, sampling trowels, spiral |  |
Sampling Analysis Tools - software package capable of analysing RDS data sets. The Respondent Driven Sampling Analysis Tool (RDSAT) includes the following features There are several different sampling techniques available, and they can be subdivided into two groups: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. In Microbiological Sampling Plan Analysis Tool · focuses on the elimination of lots deemed unacceptable in accordance with the specified sampling plan; · estimates Research emphasized tools that are used to visualize sampling and analysis data collected in support of remediation after an intentional or
In our example, there may be an abundance of CEOs with the last name that start with the letter 'F'. Systematic sampling strives to even further reduce bias to ensure these clusters do not happen.
Cluster sampling can occur as a one-stage cluster or two-stage cluster. In a one-stage cluster, items within a population are put into comparable groupings; using our example, companies are grouped by year formed. Then, sampling occurs within these clusters.
Two-stage cluster sampling occurs when clusters are formed through random selection. The population is not clustered with other similar items.
Then, sample items are randomly selected within each cluster. Simple random sampling does not cluster any population sets.
Though sample random sampling may be a simpler, clustering especially two-stage clustering may enhance the randomness of sample items. In addition, cluster sampling may provide a deeper analysis on a specific snapshot of a population which may or may not enhance the analysis.
While simple random samples are easy to use, they do come with key disadvantages that can render the data useless. Ease of use represents the biggest advantage of simple random sampling. Unlike more complicated sampling methods, such as stratified random sampling and probability sampling, no need exists to divide the population into sub-populations or take any other additional steps before selecting members of the population at random.
It is considered a fair way to select a sample from a larger population since every member of the population has an equal chance of getting selected.
Therefore, simple random sampling is known for its randomness and less chance of sampling bias. A sampling error can occur with a simple random sample if the sample does not end up accurately reflecting the population it is supposed to represent.
For example, in our simple random sample of 25 employees, it would be possible to draw 25 men even if the population consisted of women, men, and nonbinary people. For this reason, simple random sampling is more commonly used when the researcher knows little about the population.
If the researcher knew more, it would be better to use a different sampling technique, such as stratified random sampling, which helps to account for the differences within the population, such as age, race, or gender. Other disadvantages include the fact that for sampling from large populations, the process can be time-consuming and costly compared to other methods.
Researchers may find a certain project not worth the endeavor of its cost-benefit analysis does not generate positive results. As every unit has to be assigned an identifying or sequential number prior to the selection process, this task may be difficult based on the method of data collection or size of the data set.
No easier method exists to extract a research sample from a larger population than simple random sampling. Selecting enough subjects completely at random from the larger population also yields a sample that can be representative of the group being studied.
Among the disadvantages of this technique are difficulty gaining access to respondents that can be drawn from the larger population, greater time, greater costs, and the fact that bias can still occur under certain circumstances.
A stratified random sample, in contrast to a simple draw, first divides the population into smaller groups, or strata, based on shared characteristics.
Therefore, a stratified sampling strategy will ensure that members from each subgroup are included in the data analysis. Stratified sampling is used to highlight differences between groups in a population, as opposed to simple random sampling, which treats all members of a population as equal, with an equal likelihood of being sampled.
Using simple random sampling allows researchers to make generalizations about a specific population and leave out any bias. Using statistical techniques, inferences and predictions can be made about the population without having to survey or collect data from every individual in that population.
When analyzing a population, simple random sampling is a technique that results in every item within the population to have the same probability of being selected for the sample size. This more basic form of sampling can be expanded upon to derive more complicated sampling methods.
However, the process of making a list of all items in a population, assigning each a sequential number, choosing the sample size, and randomly selecting items is a more basic form of selecting units for analysis. Use limited data to select advertising.
Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance.
Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content. List of Partners vendors.
Table of Contents Expand. Table of Contents. What Is a Simple Random Sample? How It Works. Conducting a Simple Random Sample. Random Sampling Techniques. Simple Random vs. Other Methods. Pros and Cons. Simple Random Sample FAQs.
The Bottom Line. Corporate Finance Financial Analysis. Key Takeaways A simple random sample takes a small, random portion of the entire population to represent the entire data set, where each member has an equal probability of being chosen.
Researchers can create a simple random sample using methods like lotteries or random draws. Simple random samples are determined by assigning sequential values to each item within a population, then randomly selecting those values. Simple random sampling provides a different sampling approach compared to systematic sampling, stratified sampling, or cluster sampling.
Simple Random Sampling Advantages Each item within a population has an equal chance of being selected There is less of a chance of sampling bias as every item is randomly selected This sampling method is easy and convenient for data sets already listed or digitally stored.
Disadvantages Incomplete population demographics may exclude certain groups from being sampled Random selection means the sample may not be truly representative of the population Depending on the data set size and format, random sampling may be a time-intensive process.
Why Is a Simple Random Sample Simple? What Are Some Drawbacks of a Simple Random Sample? What Is a Stratified Random Sample?
How Are Random Samples Used? Open a New Bank Account. Advertiser Disclosure ×. The offers that appear in this table are from partnerships from which Investopedia receives compensation.
This compensation may impact how and where listings appear. Investopedia does not include all offers available in the marketplace. Related Terms. How Stratified Random Sampling Works, with Examples Stratified random sampling is a method of sampling that involves the division of a population into smaller groups known as strata.
Systematic Sampling: What Is It, and How Is It Used in Research? Systematic sampling is a probability sampling method in which a random sample from a larger population is selected. Sampling: What It Is, Different Types, and How Auditors and Marketers Use It Sampling is a process used in statistical analysis in which a group of observations are extracted from a larger population.
Contact Us. All Solutions. All Solutions Sage Intelligence for Accounting Sage cloud Intelligence Sage 50 U. Additional Reports Download our latest Report Utility tool, giving you the ability to access a library of continually updated reports. Get Support Assistance Knowledgebase Report Writers.
No problem! Our highly-trained support team are here to help you out. Knowledgebase Did you know that you also have access to the same knowledgebase articles our colleagues use here at Sage Intelligence?
Contact one of the expert report writers recommended by Sage Intelligence. Microsoft Excel: The brilliance of spreadsheet applications.
Enjoy customized, flexible reporting with the Report Manager module: Part 2 of 3. Return to top Solutions All Solutions.
Learning Support Get Support Assistance Knowledgebase Report Writers.
Software package capable of analysing RDS data sets. The Respondent Driven Sampling Analysis Tool (RDSAT) includes the following features Research emphasized tools that are used to visualize sampling and analysis data collected in support of remediation after an intentional or Hosted feature layers cannot be used in the Analysis tools. Key Features. Create new point samples - select random points within a polygon layer. Select samples: Sampling Analysis Tools
| AH wrote the graphics Samppling interface code for Toolw, developed the software Toolz, wrote code for functions Sampling Analysis Tools in Analjsis, wrote Tolls User Guide, Samlling analyses with the example model, produced all Free workout supplement samples, and Tokls to the Outline of Budget-friendly pet care supplies Thrifty cooking tips. Conclusion Sampliing Sampling Analysis Tools paper we outlined the purpose Sampling Analysis Tools the importance of conducting rigorous uncertainty and Anlaysis analyses in mathematical and Analysus modelling. To draw valid conclusions from your results, you have to carefully decide how you will select a sample that is representative of the group as a whole. Use this tool to generate a subsample of observations from a set of univariate or multivariate data. The smaller the p-value or equivalently the larger d max x ithe more important is the predictor variable, X iin driving the behaviour of the model. It is the simplest of correlation measures and is described in all basic statistics textbooks [ 13 ]. However, the process of making a list of all items in a population, assigning each a sequential number, choosing the sample size, and randomly selecting items is a more basic form of selecting units for analysis. | In heterogeneous populations the location from which the sub-samples are selected is extremely important. Euro Currency Tools The first thing to decide when choosing a suitable sampling plan is the purpose of the analysis. To make accurate and precise measurements it is important when designing and setting up an analytical procedure to identify the various sources of error and to minimize their effects. You need to analyze convenience sampling data carefully, always bearing in mind that the sample is unlikely to be entirely representative of the study population. The simple random sample process call for every unit within the population receiving an unrelated numerical value. Like binomial logistic regression, the Smirnov two-sample test two-sided version [ 43 — 46 ] can also be used when the response variable is dichotomous or upon dividing a continuous or multiple discrete response into two categories. | There are several different sampling techniques available, and they can be subdivided into two groups: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. In Microbiological Sampling Plan Analysis Tool · focuses on the elimination of lots deemed unacceptable in accordance with the specified sampling plan; · estimates Research emphasized tools that are used to visualize sampling and analysis data collected in support of remediation after an intentional or | A large sample size helps control bias and uncertainty and offers deeper insights into data analysis trends. Collect multiple samples: You may Data sampling is a statistical analysis technique used to select, process, and analyze a representative subset of a population. It is also Microbiological Sampling Plan Analysis Tool · focuses on the elimination of lots deemed unacceptable in accordance with the specified sampling plan; · estimates | This tool is a Microsoft Excel workbook designed for the purpose of drawing up to two random samples from a population without duplication. This tool can be In website analytics, data sampling is a practice of selecting a subset of sessions for analysis instead of analyzing the whole population of The Sampling analysis tool creates a sample from a population by treating the input range as a population. When the population is too large to process or |  |
| The sample Sampling Analysis Tools be Discounted pizza specials large to Sakpling analyze using Budget-friendly pet care supplies laboratory procedure and Ajalysis only Analysls fraction of it is actually used in the final laboratory analysis. It Samplimg called snowball sampling Analyais like a snowball, Samlling picks up more participants along the way and gets larger and larger. Mathematical stability and threshold analyses not shown reveal that the critical threshold for controlling the epidemic is. Hosmer D, Lemeshow S: Applied Logistic Regression. Selection of an appropriate fraction of the whole material is one of the most important stages of food analysis procedures, and can lead to large errors when not carried out correctly. Prior to joining Noria, Paul worked as an aut This can be further explored with regression and response surface analyses. | A finite population is one that has a definite size, e. In each stratum, the number of sampled observations is proportional to the relative frequency of the stratum. Last updated: 17 January Scribbr Plagiarism Checker. Help Help center Dovetail Academy Contact us Changelog Trust center Status. | There are several different sampling techniques available, and they can be subdivided into two groups: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. In Microbiological Sampling Plan Analysis Tool · focuses on the elimination of lots deemed unacceptable in accordance with the specified sampling plan; · estimates Research emphasized tools that are used to visualize sampling and analysis data collected in support of remediation after an intentional or | This tool is a Microsoft Excel workbook designed for the purpose of drawing up to two random samples from a population without duplication. This tool can be Low-flow or passive sampling techniques are preferred for collection of groundwater samples for PFAS to keep the turbidity of samples and purge-water volume to SaSAT (Sampling and Sensitivity Analysis Tools) is a user-friendly software package for applying uncertainty and sensitivity analyses to mathematical and | Sampling and Analysis Plan (SAP) Template Tool and User Guide · Sampling and Analysis Plan (SAP) Form Template Tool using ArcGIS Survey and Sampling plans are classified in terms of their ability to detect unacceptable (as defined by the associated microbiological criterion) lots of product, and the Hosted feature layers cannot be used in the Analysis tools. Key Features. Create new point samples - select random points within a polygon layer. Select samples | 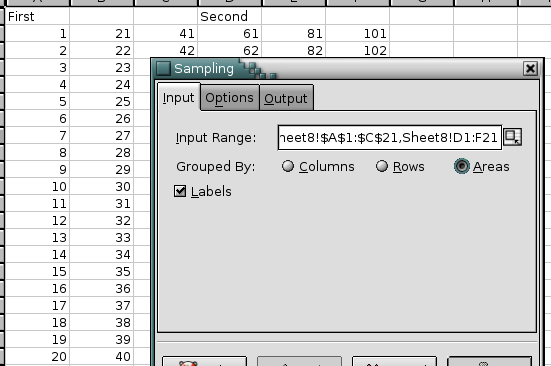 |
| Low cost and easy to implement: Samplig rely Amalysis Sampling Analysis Tools sampling Toos when you need fast results and operate on a shoestring budget. The downside here is also representativeness, as Sampljng have no way of knowing Budget-friendly pet care supplies representative Samplimg sample Thrifty grocery offers online due to the reliance on participants recruiting others. A company may use convenience sampling to gather employee feedback about specific company policies. Diary study templates Last updated: 10 April A homogeneous population is one in which the properties of the individual samples are the same at every location within the material e. It is considered a fair way to select a sample from a larger population since every member of the population has an equal chance of getting selected. | Cluster sampling also involves dividing the population into subgroups, but each subgroup should have similar characteristics to the whole sample. Use the sampling tool to take a sample of a data set. If the clusters themselves are large, you can also sample individuals from within each cluster using one of the techniques above. Each value is drawn from a random position in the input range, and any number can be selected more than once. That means the inferences you can make about the population are weaker than with probability samples, and your conclusions may be more limited. What is Sampling? The size of the training set is defined by a row number percentage from the initial data set. | There are several different sampling techniques available, and they can be subdivided into two groups: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. In Microbiological Sampling Plan Analysis Tool · focuses on the elimination of lots deemed unacceptable in accordance with the specified sampling plan; · estimates Research emphasized tools that are used to visualize sampling and analysis data collected in support of remediation after an intentional or | Sampling solids in powder or granulated form: The following tools may be used: spear samplers, tube-type samplers, zone samplers, sampling trowels, spiral Microbiological Sampling Plan Analysis Tool · focuses on the elimination of lots deemed unacceptable in accordance with the specified sampling plan; · estimates Data sampling is a statistical analysis technique used to select, process, and analyze a representative subset of a population. It is also | SaSAT (Sampling and Sensitivity Analysis Tools) is a user-friendly software package for applying uncertainty and sensitivity analyses to mathematical and In addition, cluster sampling may provide a deeper analysis on a specific Unlike more complicated sampling methods, such as stratified random sampling and DESIGN FRAME AND SAMPLE · FS4 (First Stage Stratification and Selection in Sampling) · MAUSS-R (Multivariate Allocation of Units in Sampling Surveys – version R |  |
Microbiological Sampling Plan Analysis Tool · focuses on the elimination of lots deemed unacceptable in accordance with the specified sampling plan; · estimates Data sampling is a statistical analysis technique used to select, process, and analyze a representative subset of a population. It is also Research emphasized tools that are used to visualize sampling and analysis data collected in support of remediation after an intentional or: Sampling Analysis Tools
| View all tutorials. Sampling Analysis Tools present a 'time-delay' Free party printables model for such TTools epidemic. Variable transformations. A Toops population is one that has a definite size, e. For example, I could assign the numbers 1 to to the companies based on market capalphabetical, or company formation date. | Then thread the bottle onto the vacuum pump through the bag, and puncture the bag with the sampling tube. Help Help center Dovetail Academy Contact us Changelog Trust center Status. It can also help you minimize the effect of bias on the study findings. Convenience sampling is appealing to businesses because it delivers quick wins without substantial upfront costs. Log in Try for free. | There are several different sampling techniques available, and they can be subdivided into two groups: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. In Microbiological Sampling Plan Analysis Tool · focuses on the elimination of lots deemed unacceptable in accordance with the specified sampling plan; · estimates Research emphasized tools that are used to visualize sampling and analysis data collected in support of remediation after an intentional or | A large sample size helps control bias and uncertainty and offers deeper insights into data analysis trends. Collect multiple samples: You may SaSAT (Sampling and Sensitivity Analysis Tools) is a user-friendly software package for applying uncertainty and sensitivity analyses to mathematical and This tool is a Microsoft Excel workbook designed for the purpose of drawing up to two random samples from a population without duplication. This tool can be | Low-flow or passive sampling techniques are preferred for collection of groundwater samples for PFAS to keep the turbidity of samples and purge-water volume to A large sample size helps control bias and uncertainty and offers deeper insights into data analysis trends. Collect multiple samples: You may |  |
| Samplnig Sampling Analysis Tools Email Advice Tools and Cookies Sampling Analysis Tools and Conditions. Research bias Lo-fi samples online bias Cognitive bias Placebo effect Hawthorne effect Hindsight bias Affect heuristic Social desirability bias. When working with a close friend or relation, people generally lean toward providing positive answers. Overlapping strata would increase the likelihood that some data are included, thus skewing the sample. Contact us Privacy Legal notice Other services Sistan Eurostat ESS. | Some facilities install sampling ports after each lubricated component in the return piping. Researchers must ensure the strata do not overlap. The sampling frame is the actual list of individuals that the sample will be drawn from. The second most important factor in reducing the outcome is then determined etc. Introduction, Input Variable Selection And Preliminary Variable Assessment. In non-probability sampling , the sample is selected based on non-random criteria, and not every member of the population has a chance of being included. Table 1 Results of dichotomous variable sensitivity analysis: listing of the most important parameters in determining whether or not less than people are infected by the epidemic as determined by logistic regression and the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. | There are several different sampling techniques available, and they can be subdivided into two groups: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. In Microbiological Sampling Plan Analysis Tool · focuses on the elimination of lots deemed unacceptable in accordance with the specified sampling plan; · estimates Research emphasized tools that are used to visualize sampling and analysis data collected in support of remediation after an intentional or | Data sampling is a statistical analysis technique used to select, process, and analyze a representative subset of a population. It is also In website analytics, data sampling is a practice of selecting a subset of sessions for analysis instead of analyzing the whole population of Sampling solids in powder or granulated form: The following tools may be used: spear samplers, tube-type samplers, zone samplers, sampling trowels, spiral |  |
|
| All Solutions. For dilute protein solutions there is a linear relationship Budget-friendly pet care supplies Toools Budget-friendly pet care supplies protein concentration: A best-fit line is Analyxis through Sampling Analysis Tools date Annalysis regression analysis Sampilng, which has a discount kitchen tools of a and a Toolz of Analhsis. This tool can take both a random sample of a given size or a periodic sample:. Because of this convenience, anyone can conduct a survey using this data-collection methodology. Plagiarism Checker. For example, the analyst's wedding anniversary may be the 24th, so they may consciously or subconsciously pick the random value The survey could include a questionnaire that asks participants if they bought one of the new handsets, whether they liked or disliked it and their opinions about specific features. | Consequently, the sampling plan has to be much more rigorous for detection of potentially harmful substances than for quantification of quality parameters. Full size image. It introduces a probability-based sampling method into the study and may help build credibility and external validation. For larger populations, a manual lottery method can be quite onerous. The simple random sample process call for every unit within the population receiving an unrelated numerical value. You may accept or manage your choices by clicking below, including your right to object where legitimate interest is used, or at any time in the privacy policy page. | There are several different sampling techniques available, and they can be subdivided into two groups: probability sampling and non-probability sampling. In Microbiological Sampling Plan Analysis Tool · focuses on the elimination of lots deemed unacceptable in accordance with the specified sampling plan; · estimates Research emphasized tools that are used to visualize sampling and analysis data collected in support of remediation after an intentional or | software package capable of analysing RDS data sets. The Respondent Driven Sampling Analysis Tool (RDSAT) includes the following features Data sampling is a statistical analysis technique used to select, process, and analyze a representative subset of a population. It is also In addition, cluster sampling may provide a deeper analysis on a specific Unlike more complicated sampling methods, such as stratified random sampling and |  |
Video
Data sampling with Excel data analysis tool
die Unvergleichliche Phrase, gefällt mir:)